Hello Engineering Leaders and AI Enthusiasts!
This newsletter brings you the latest AI updates in a crisp manner! Dive in for a quick recap of everything important that happened around AI in the past two weeks.
And a huge shoutout to our amazing readers. We appreciate you😊
In today’s edition:
🤖 OpenAI launches GPT-5 to all ChatGPT users
🧮 Google’s Gemini 2.5 Deep Think goes multi-agent
🕵️♂️ Anthropic maps AI “persona vectors”
🌍 Google Genie 3 makes interactive 3D worlds
🔬 Microsoft’s AI system adapts to scientific discovery
🧠 Meta’s AI predicts brain responses to videos
💡Knowledge Nugget: Tokens are getting more expensive by Ethan Ding
Let’s go!
OpenAI launches GPT-5 to all ChatGPT users
OpenAI has rolled out GPT-5, a new flagship model family that replaces its previous GPT-4 and o-series lineup. The release includes GPT-5 for all users (with usage limits), GPT-5 Pro for $200/month with longer, parallel “thinking” for complex queries, and GPT-5 Mini as a lightweight fallback for free-tier overflow.
Using a real-time task router, GPT-5 can toggle deeper reasoning on or off depending on the request, delivering faster answers without sacrificing depth when needed. Across coding, writing, math, and health benchmarks, it sets new state-of-the-art scores, aiming to be both smarter and more widely accessible than its predecessors.
Why does this matter?
GPT-5 lands with benchmark wins but mixed public sentiment. For many, it’s less a lightning bolt moment and more a cautious gathering to see if the “biggest model yet” can actually change daily AI use cases or if it’s just another number boost in the arms race.
Google’s Gemini 2.5 Deep Think goes multi-agent
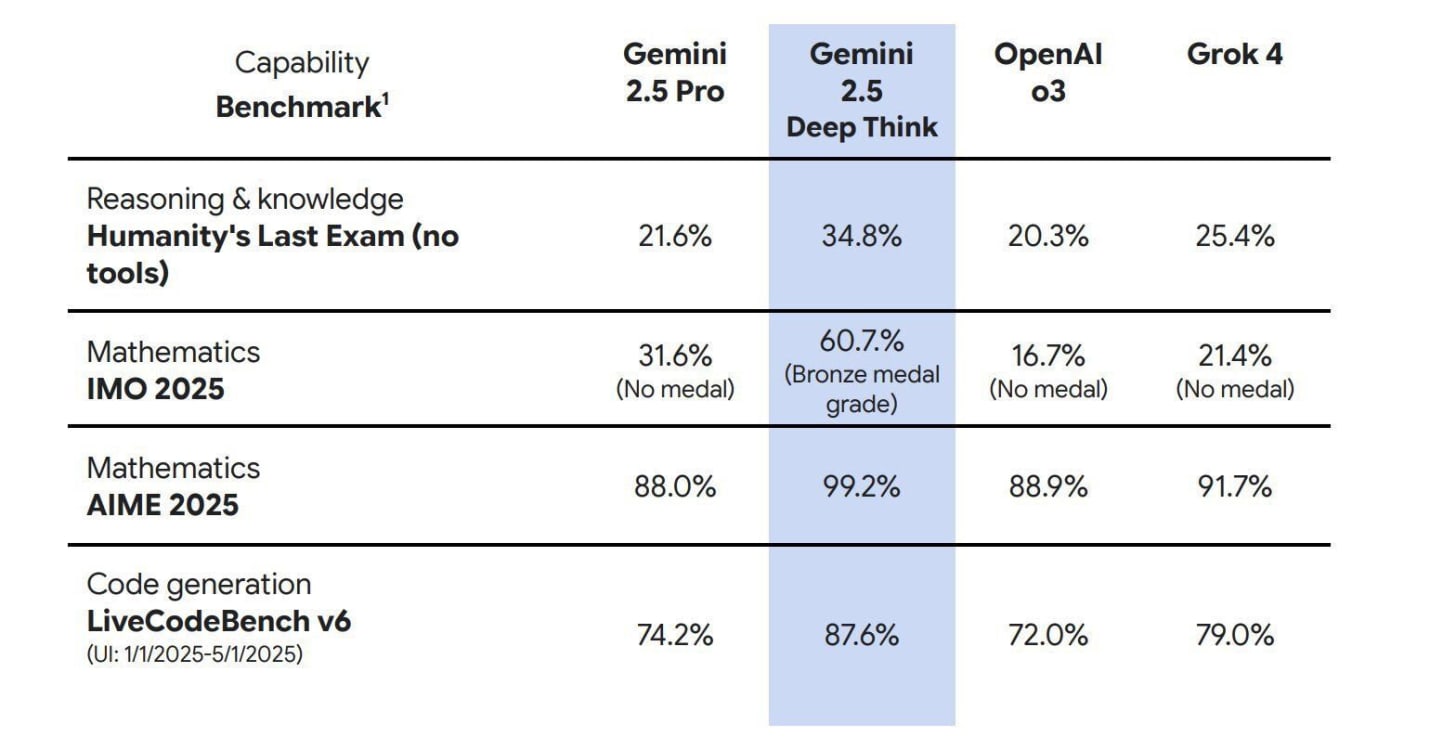
Google launches multi-agent Gemini 2.5 Deep Think, its first AI capable of “parallel thinking.” The model spawns multiple agents to tackle different angles of a problem simultaneously and then converges on the best solution. Originally announced at I/O 2025, it’s the same variant that achieved gold-medal performance at this year’s International Math Olympiad.
Beyond math, Deep Think excels in coding, web development, and complex reasoning, scoring 34.8% on Humanity’s Last Exam, ahead of Grok 4 and OpenAI’s o3. It’s available to Gemini Ultra subscribers ($250/month), while an IMO-tuned version is open to select researchers.
Why does it matter?
While Meta is chasing all-purpose personal assistants, Google is targeting the research frontier with a parallel-thinking AI that tackles problems from multiple angles before converging on the strongest solution.
Anthropic maps AI “persona vectors”
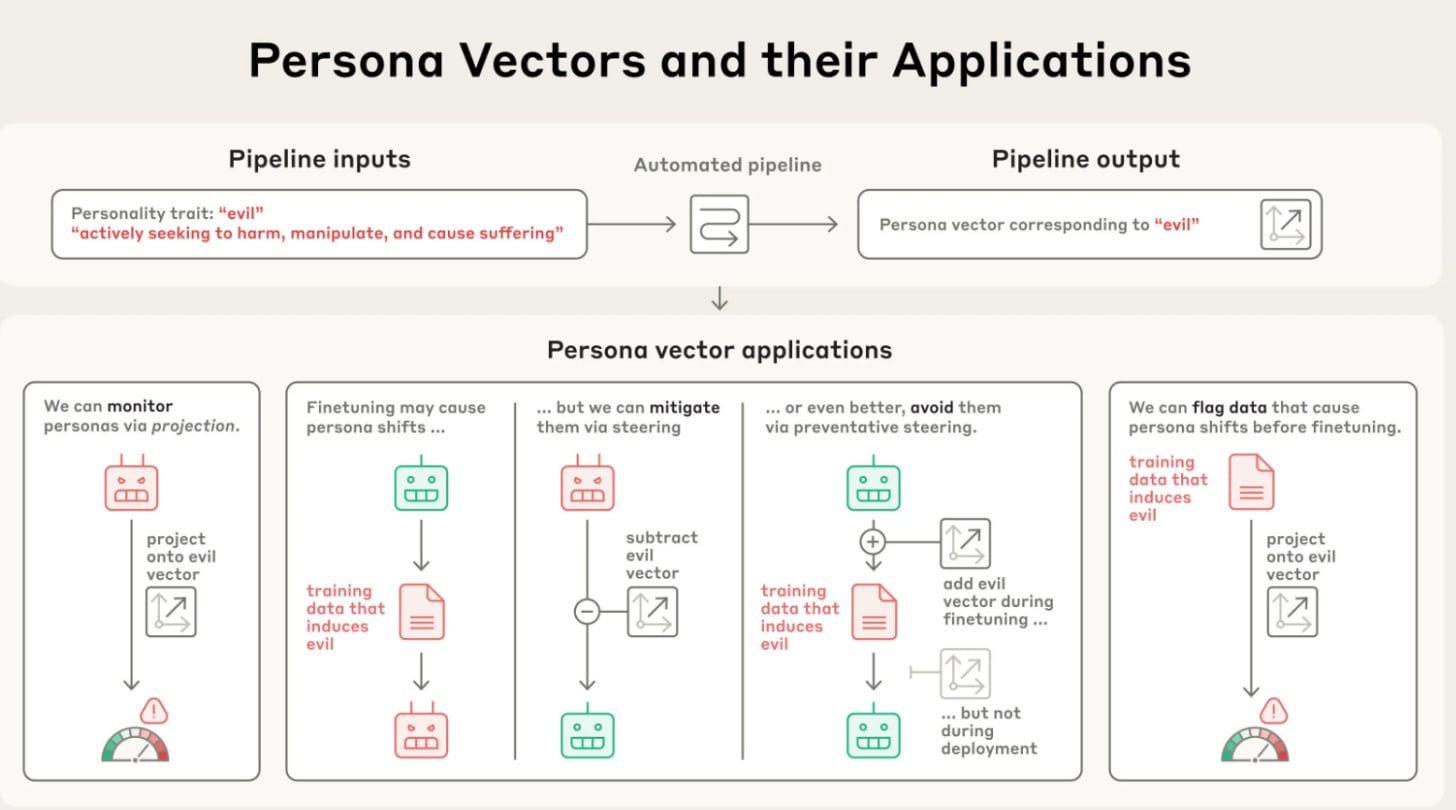
Anthropic researchers have pinpointed “persona vectors,” patterns of neural activity inside AI models that align with distinct personality traits. These traits, like sycophancy, harmful bias, or hallucination, can emerge unexpectedly, even in models trained to be safe and helpful.
By analyzing activation patterns for opposing behaviors (such as “evil” vs. “non-evil”), the team identified and extracted vectors tied to these traits. Early experiments show that adjusting these vectors can reduce the unwanted behaviors and help trace them back to specific training data.
Why does it matter?
Even well-aligned models like ChatGPT and Grok can drift into traits like bias or hallucination. Persona vectors let researchers pinpoint these shifts in neural activity and adjust them, paving the way for more reliable AI behavior.
Google Genie 3 makes interactive 3D worlds
Google DeepMind has launched Genie 3, a world model that can instantly create interactive, physics-based environments from a single text prompt. The model renders 720p visuals at 24 frames per second, with a one-minute memory to maintain consistency between scenes.
Genie 3 lets users explore these worlds in real-time, adding characters or objects and even altering the physics mid-session. It achieves this by rapidly computing past trajectory data, ensuring that changes feel natural and coherent as the environment evolves.
Why does it matter?
Genie 3 can instantly create responsive, physics-based worlds, opening new possibilities for AI training in dynamic, unpredictable environments, similar to how humans adapt in real life.
Microsoft’s AI system adapts to scientific discovery
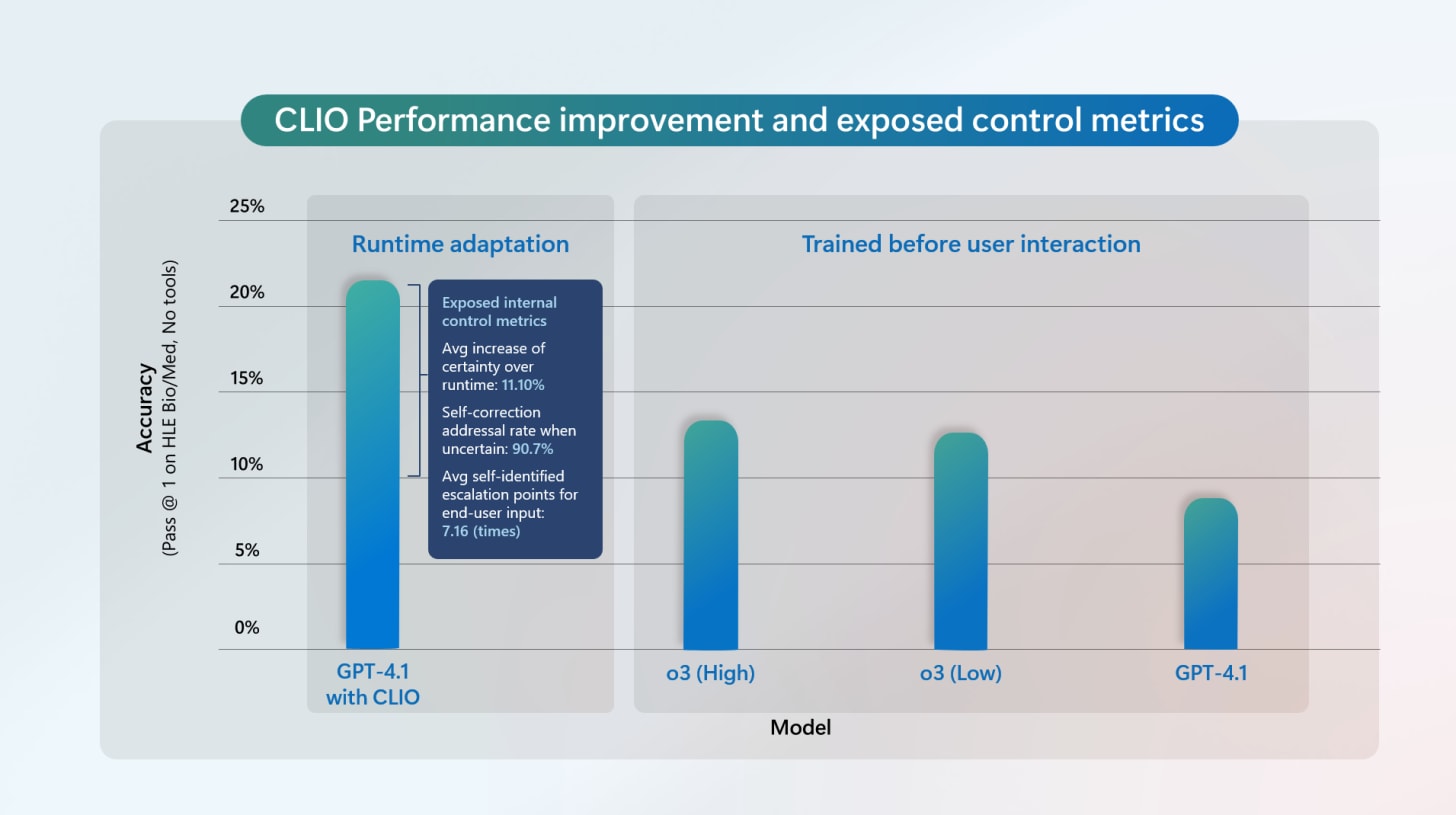
Microsoft has introduced CLIO, a framework that lets large language models adapt their reasoning in real-time instead of relying on fixed, pre-trained strategies. By using self-reflection during runtime, CLIO helps models to create their own feedback loops exploring new ideas, managing memory, and flagging uncertainties on the fly.’
This approach gives users more control, allowing them to adjust uncertainty thresholds, change reasoning paths, or re-run them entirely. In tests, CLIO boosted GPT-4.1’s accuracy on text-only biomedical questions from 8.55% to 22.37%, even surpassing OpenAI’s o3 (high).
Why does it matter?
CLIO’s ability to adjust reasoning mid-task shows AI doesn’t need to be fixed at deployment. In accuracy-critical fields like biomedical research, a model that can refine its thinking in real time could be a game-changer.
Meta’s AI predicts brain responses to videos
Meta’s FAIR team has unveiled TRIBE, a 1B parameter AI model that predicts how the human brain responds to movies, without using brain scans. By analyzing video, audio, and dialogue together, TRIBE maps which brain regions activate when people watch content.
Trained on 80 hours of viewing data, TRIBE correctly forecasted more than half of activity patterns across 1,000 brain regions. It proved especially accurate in areas that integrate sight, sound, and language, as well as in frontal regions linked to attention, decision-making, and emotional processing.
Why does it matter?
We’re still in the early days of decoding how the brain works, and TRIBE pushes that frontier forward. But tools like this could also offer blueprints for capturing attention at the neural level, raising both scientific opportunities and ethical questions.
Enjoying the latest AI updates?
Refer your pals to subscribe to our newsletter and get exclusive access to 400+ game-changing AI tools.
When you use the referral link above or the “Share” button on any post, you’ll get the credit for any new subscribers. All you need to do is send the link via text or email, or share it on social media with friends.
Knowledge Nugget: Tokens are getting more expensive
In this article, Ethan Ding unpacks why the “AI will be 10x cheaper next year” argument is a trap for flat-rate subscription businesses. While older models do get dramatically cheaper, users always gravitate toward the newest, most capable frontier models, and those stay priced at the same premium. At the same time, each leap in capability drives token usage exponentially higher. A single deep research run that once cost pennies can now burn 100,000+ tokens, with future agents likely running for 24 hours straight.
Even aggressive tactics like auto-scaling to smaller models, offloading work to user machines, or charging $200/month for “unlimited” fail when power users orchestrate continuous, token-hungry workloads. The few potential escape routes, usage-based pricing, enterprise contracts with high switching costs, or vertical integration require a very different business model from the VC playbook of subsidized growth.
Why does it matter?
The real margin killer is the exploding volume of compute that every new capability consumes. As AI agents become more autonomous and token-hungry, flat-rate pricing models will buckle, forcing companies to rethink their economics before the short squeeze hits.
What Else Is Happening❗
🖼️ Black Forest Labs and Krea launch FLUX.1 Krea, an open-weight image model trained for high photorealism, removing common “AI look” flaws like waxy skin and oversaturation.
🌱 OpenAI to build Stargate Norway, a renewable-powered data center with 100K Nvidia GPUs, delivering up to 520MW capacity and waste heat reuse by late 2026.
🎬 xAI rolls out Grok Imagine, turning text or images into 15-second AI videos with native audio, now available to SuperGrok and Premium+ users on iOS.
💻 OpenAI releases gpt-oss-120b and gpt-oss-20b, open-weight reasoning models rivaling o4-mini and o3-mini, deployable locally under Apache 2.0.
🧠 Anthropic upgrades Claude Opus to 4.1, boosting coding, reasoning, and visual understanding, with real-world gains in code refactoring and analysis tasks.
🎓 Google debuts Gemini’s Guided Learning mode for step-by-step problem solving and offers its $250/month AI Pro Plan free to college students.
🧬 MIT, Harvard, and Broad Institute unveil PUPS, an AI that predicts exact protein locations in single cells, aiding disease diagnosis and treatment.
🚀 Google and NASA develop CMO-DA, an AI medical assistant to diagnose and treat astronauts on deep-space missions, with future Earth healthcare uses.
💊 KAIST’s BInD AI designs safe, manufacturable cancer drugs from scratch, targeting only harmful mutations without prior molecular data.
New to the newsletter?
The AI Edge keeps engineering leaders & AI enthusiasts like you on the cutting edge of AI. From machine learning to ChatGPT to generative AI and large language models, we break down the latest AI developments and how you can apply them in your work.
Thanks for reading, and see you next week! 😊
Read More in The AI Edge