OpenAI completed its for-profit restructuring — and struck a new deal with Microsoft
OpenAI finalized its for-profit restructuring by converting its operating arm into a public benefit corporation called OpenAI Group PBC, while its nonprofit parent is now the OpenAI Foundation. The Foundation holds equity valued at about $130 billion, will initially deploy $25 billion toward healthcare, disease, and “AI resilience,” and will gain additional ownership after an unspecified valuation milestone.
After negotiations with California and Delaware AGs and a legal fight with Elon Musk, OpenAI shifted from a plan removing nonprofit control to one where the nonprofit keeps oversight and can own up to $100 billion of equity. A major open question remains whether the nonprofit will ultimately control core technology and any potential AGI.
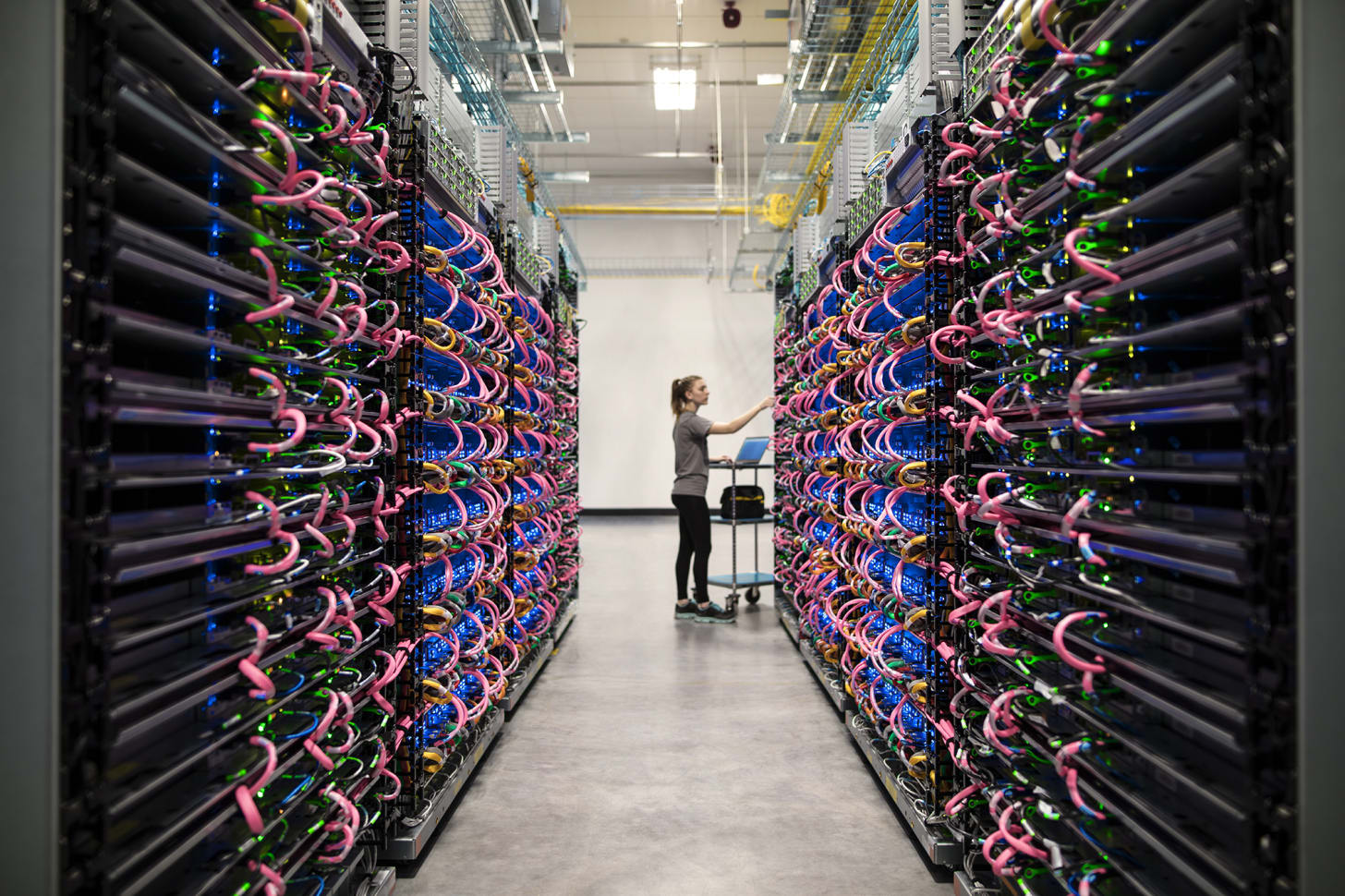
OpenAI also signed a new deal with Microsoft that reduces Microsoft’s stake to roughly 27% (as-converted diluted, valued around $135 billion) and clarifies the “AGI clause.” Any AGI declaration by OpenAI must now be verified by an independent expert panel. Microsoft’s IP rights for models and products extend through 2032 and now include post-AGI models with safety guardrails, but its rights to OpenAI’s research expire by 2030 or upon AGI verification, whichever comes first. Key carve-outs:
-
Microsoft’s IP rights do not cover OpenAI’s consumer hardware (e.g., the Jony Ive project)
-
The partnership’s exclusivity is further loosened (OpenAI can work with third parties and release some open-weight models)
-
Microsoft loses right of first refusal on compute, and OpenAI commits to an incremental $250 billion of Azure spend.
-
Microsoft can now independently pursue AGI, with compute thresholds applying if it builds on OpenAI IP before AGI is verified.
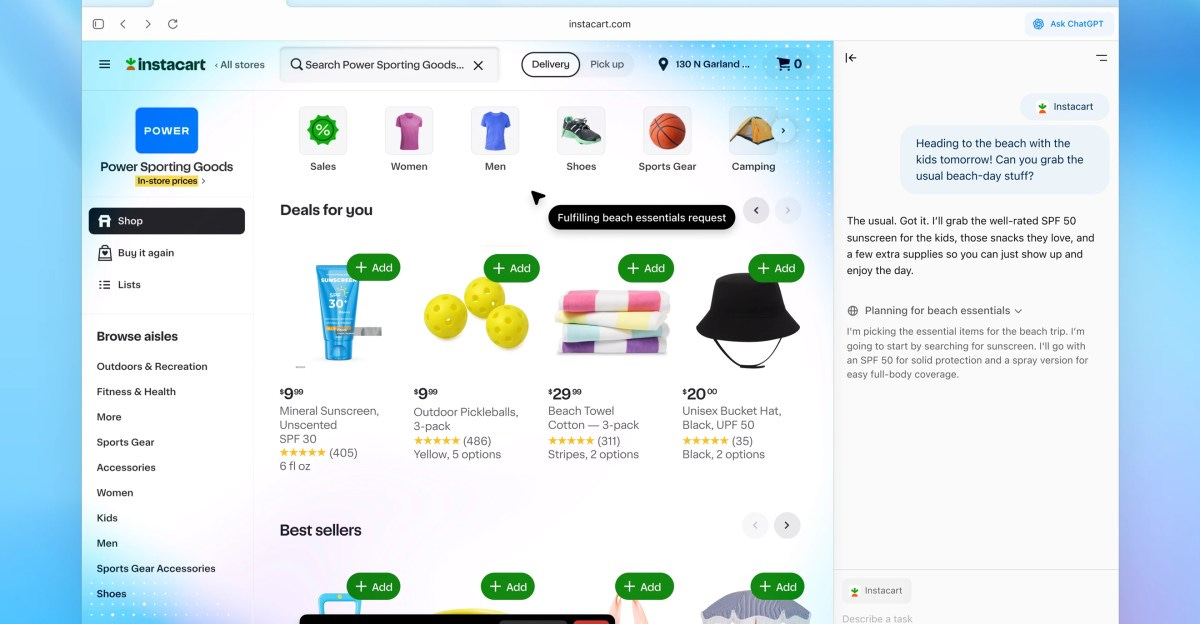
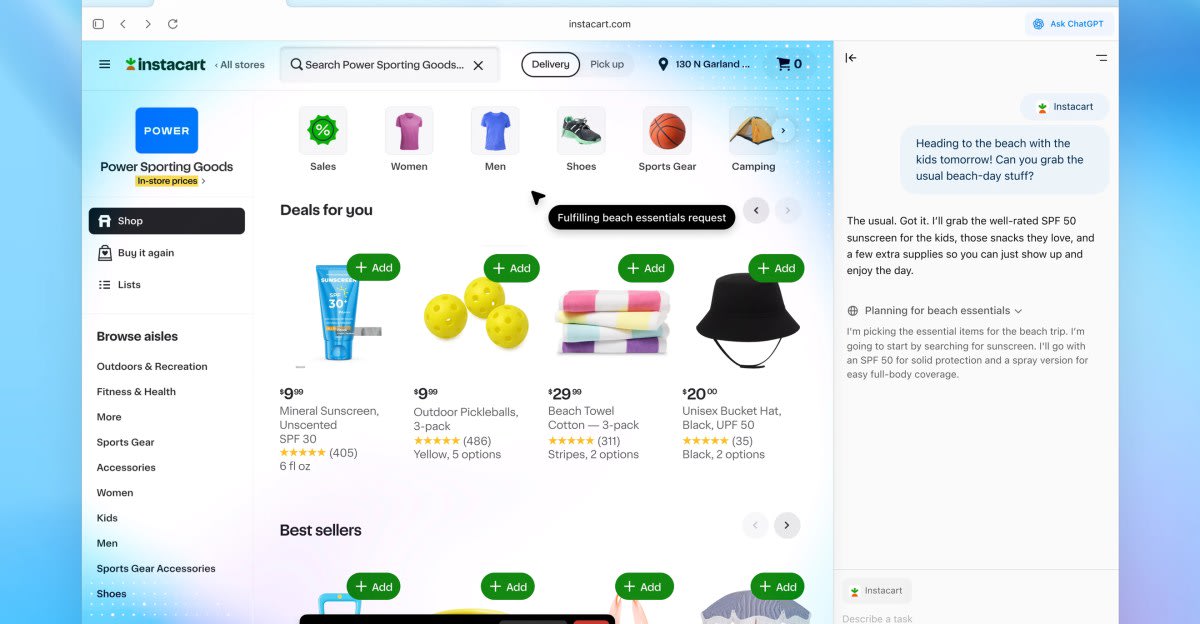
OpenAI’s AI-powered browser, ChatGPT Atlas, is here
Related:
OpenAI unveiled ChatGPT Atlas, an AI-powered web browser now available globally on macOS with Windows, iOS, and Android “coming soon.” Atlas features a persistent split-screen “companion” that pairs webpages with a live ChatGPT transcript, one-click webpage summarization, and “cursor chat” for in-line edits to selected text. It notably has:
-
Memory, which stores user-specific context to personalize browsing and can be viewed/managed in settings, plus an incognito mode
-
An “agent mode” lets ChatGPT take actions like booking reservations or editing documents, currently limited to Plus/Pro users. The product builds on OpenAI’s prior agentic experiments (Operator, ChatGPT Agent) and follows the company’s SearchGPT prototype, positioning Atlas against AI-first browsing plays from Perplexity Comet and Google’s planned Gemini-in-Chrome automations.
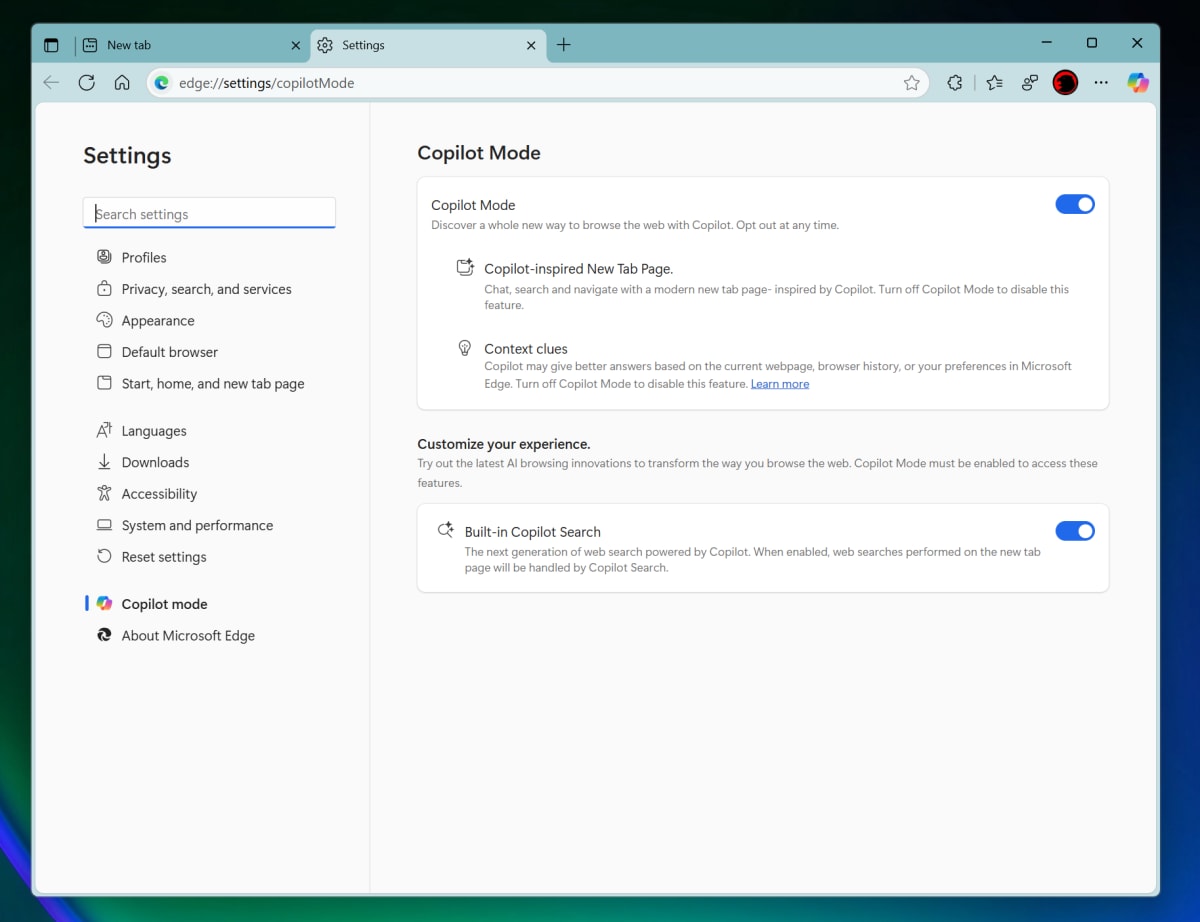
Within two days, Microsoft reintroduced Copilot Mode in Edge as an “AI browser,” adding Actions (form-filling, hotel booking) and Journeys (reasoning over open tabs) to its ride-along assistant that summarizes, compares, and acts across pages with user permission. The UI and workflow strongly echo Atlas, differing mainly in layout (new-tab panel vs split-screen) while hinging on underlying models for capability.
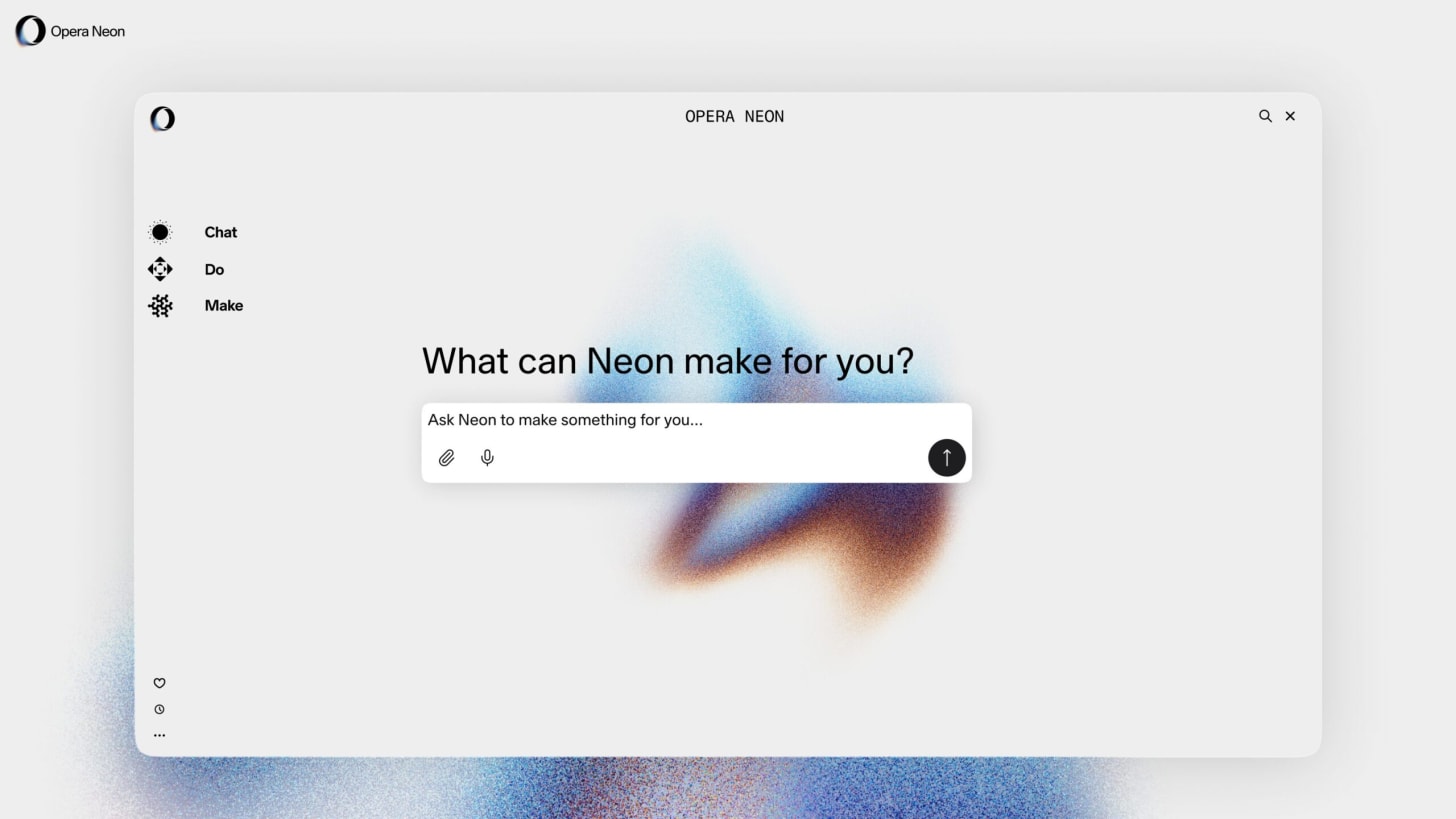
About a month ago, there was yet another browser release: Opera launched Neon, a $19.90/month AI browser that bundles three agents—Chat (QA/summarization), Do (agentic browsing to complete tasks), and Make (sandboxed tool/app builder)—plus “Cards” prompt presets; reviewers found Chat verbose and error-prone, Do unreliable and hard to steer mid-task, and Make functional but clunky.
Across launches, common themes are agentic actions (booking, form-filling), tab-aware reasoning, built-in summarization, and inline editing—but with early-stage reliability, speed, and UX trade-offs that make control, memory management, and clear tool boundaries crucial.
Google and Anthropic announce cloud deal worth tens of billions of dollars
Google and Anthropic announced a cloud partnership giving Anthropic access to up to 1 million Google Tensor Processing Units (TPUs), a multi-year commitment valued in the tens of billions of dollars. The buildout is expected to bring well over 1 gigawatt of AI compute online in 2026; industry estimates put a 1-GW data center at around $50 billion in total cost, with about $35 billion typically for chips.
Google highlighted strong price-performance and efficiency on its seventh‑generation “Ironwood” TPU accelerators, calling this Anthropic’s largest TPU commitment to date. The deal fits Anthropic’s multi-cloud strategy, where Claude models run across Google TPUs, Amazon Trainium, and Nvidia GPUs, with specific platforms optimized for training, inference, and research.
Anthropic’s compute needs are rising with rapid revenue and user growth: annual revenue run rate is nearing $7 billion, Claude is used by 300,000+ businesses (300× in two years), large $100k+ customers are up ~7× year over year, and Claude Code hit a $500 million annualized run rate within two months of launch. Despite the TPU expansion, AWS remains Anthropic’s primary cloud partner: Amazon has invested $8 billion (vs. Google’s $3 billion total to date), and Anthropic’s Project Rainier supercomputer uses Trainium 2 to reduce cost per compute by avoiding premium chip margins.
Microsoft’s Mico is a ‘Clippy’ for the AI era
Microsoft introduced Mico, a customizable animated avatar for Copilot that serves as a “face” for the AI assistant, debuting first in the U.S., Canada, and the U.K. Mico appears during voice mode by default and “listens, reacts, and changes colors,” can save memories from conversations, and learns from feedback; users can disable it. An Easter egg lets Mico transform into Clippy after repeated taps, embracing the nostalgic comparison.
Microsoft also launched “Real Talk,” a new conversational mode that mirrors a user’s style while maintaining its own perspective, designed to push back constructively rather than act sycophantically, alongside “Learn Live,” which tutors users through concepts step by step. The fall Copilot update adds multi-user chats where you can bring friends into a Copilot conversation, long-term memory, and connectors to pull context from email and cloud storage.
Other News
Tools
OpenAI made ChatGPT better at sifting through your work or school information. A GPT-5-based connector now searches multiple workplace tools like Slack, Google Drive, SharePoint, and GitHub simultaneously, returning cited, time-filtered answers and briefings for Business, Enterprise, and Education users.
Anthropic’s Claude catches up to ChatGPT and Gemini with upgraded memory features. Paid Claude users can enable editable, transparent memory spaces that persist across chats, import or export memories from rivals, and choose what the bot remembers to keep personal and work conversations separate.
Anthropic brings Claude Code to the web. The new web app, rolling out to Anthropic’s paid Pro and Max subscribers, brings the popular Claude Code agent-based coding tool from the command line to browsers and mobile so developers can create, manage, and run autonomous coding agents more widely.
DeepSeek Just Released a 3B OCR Model: A 3B VLM Designed for High-Performance OCR and Structured Document Conversion. The model compresses page images into a small set of vision tokens using a high-resolution encoder and a 3B MoE decoder to enable near-lossless OCR and structured document parsing, offering explicit token-budget modes and strong benchmarked compression/precision trade-offs.
Amazon unveils AI smart glasses for its delivery drivers. These provide hands-free package scanning, turn-by-turn walking directions, proof-of-delivery capture, and AI-powered hazard detection via cameras and a vest-mounted controller, and are being trialed in North America before a wider rollout.
Manus 1.5 and Manus-1.5-Lite debut as the newest agentic AI releases from Manus. The update reduces task times from 15 to 4 minutes, boosts output quality by about 15%, and can autonomously build, test, and refine full web applications, with the Lite edition public and the full model subscriber-only.
Adobe’s AI social media admin is here with ‘Project Moonlight’. Acting as a central, context-aware assistant, Moonlight links Creative Cloud libraries and social accounts to coordinate Adobe’s app-specific AI tools, generate content from conversations, and analyze performance to suggest strategy.
Yelp’s AI can now take reservations over the phone. The company is rolling out 24/7 virtual staff that can answer calls, take or modify reservations, manage waitlists, send order or menu links via text, and handle basic customer queries for restaurants and other local businesses starting at $99–$149 per month.
Facebook’s AI can now suggest edits to the photos still on your phone. Opt-in users’ camera-roll photos are uploaded to Meta’s cloud for AI-powered suggestions like collages, restyles, and recaps; Meta says images won’t be used to train models or target ads unless edited or shared.
Business
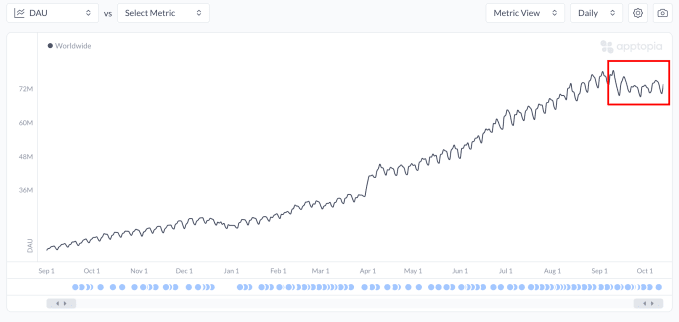
ChatGPT’s mobile app is seeing slowing download growth and daily use, analysis shows. Analysis from Apptopia indicates new download growth and U.S. engagement metrics (time spent and sessions per user) have declined or stabilized since spring, suggesting novelty-driven expansion is fading and retention is now limited to core users.
Top OpenAI, Google Brain researchers set off a $300M VC frenzy for their startup Periodic Labs. The founders are using their $300M seed to build an AI-driven materials-science company that combines simulations, LLM-guided experiment planning, and (soon-to-be-trained) robotic wet labs to discover new materials like superconductors, while also generating valuable experimental data.
Anthropic launches Claude Life Sciences to give researchers an AI efficiency boost. The tool integrates Claude models with lab platforms like Benchling, PubMed, and 10x Genomics to assist researchers across discovery workflows—from literature review and data analysis to drafting regulatory submissions—so routine tasks can be completed far faster.
OpenEvidence, the ChatGPT for doctors, raises $200M at $6B valuation. Trained on major medical journals, the startup offers a free, ad-supported platform for verified clinicians to quickly retrieve evidence-based answers and has grown to about 15 million clinical consultations per month.
OpenAI Cofounder Karpathy Says Great AI Agents Are Still a Decade Away. But There’s Magic to Be Had in Incremental Work.. Karpathy argues that while current agentic and coding AIs are useful, they lack continual learning and robustness, so meaningful, widely deployed intelligent agents will require years of incremental engineering and integration rather than an imminent AGI breakthrough.
Meta Cutting Roughly 600 AI Jobs as Company Aims to Move Faster. The layoffs affect about 600 employees in Meta Superintelligence Labs as the company restructures to speed up AI development, while sparing its newly formed TBD Lab and recent high-paid hires.
Research
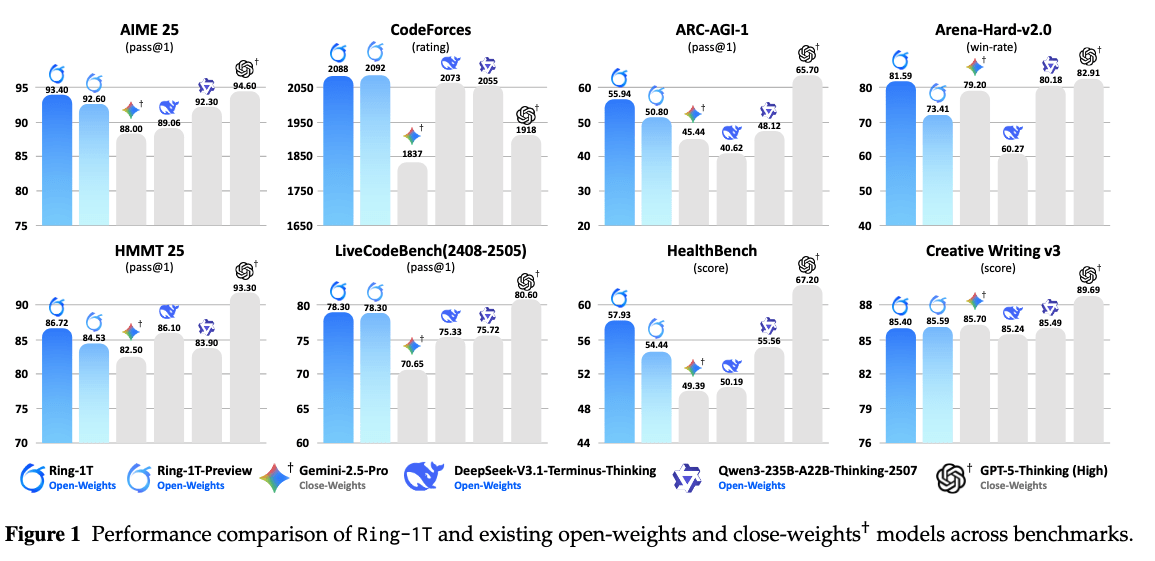
Every Step Evolves: Scaling Reinforcement Learning for Trillion-Scale Thinking Model. The team introduces Ring-1T, a trillion-parameter open-source model trained with new systems (IcePop, C3PO++, ASystem) that achieves leading benchmark results and aims to make large-scale reasoning more accessible.
LLMs Can Get “Brain Rot”!. Researchers find that chronic training on low-quality web text degrades LLMs’ reasoning, context retention, safety behaviors, and personality consistency, though instruction tuning and cleaner pretraining can partially restore performance.
The Coverage Principle: How Pre-Training Enables Post-Training. The authors argue that pre-training provides broad coverage of data and tasks, enabling efficient specialization during post-training by leveraging prior representations and reducing the need for task-specific examples.
How Do LLMs Use Their Depth?. Findings suggest that LLMs make early, high-frequency “guesses” in shallow layers that are progressively refined into context-appropriate predictions in deeper layers, with depth usage varying by token type and task complexity.
Continual Learning via Sparse Memory Finetuning. This method updates only a small subset of memory slots per step—selected by TF-IDF to rank slots by relevance—so models can learn from streams of facts or documents without the catastrophic forgetting seen in full or LoRA finetuning.
Accelerating Vision Transformers with Adaptive Patch Sizes. The approach reduces token count by assigning larger patches to low-entropy regions and smaller patches to detailed areas, using multiscale entropy to guide patch sizes and a zero-initialized MLP to preserve accuracy while cutting computation by up to ~40%.
Antislop: A Comprehensive Framework for Identifying and Eliminating Repetitive Patterns in Language Models. The framework detects repetitive phraseology in LLM outputs and reduces it through a sampler-driven pipeline and token-preference optimization while preserving model performance.
Seed3D 1.0: From Images to High-Fidelity Simulation-Ready 3D Assets. The system can generate high-detail, simulation-ready 3D assets with 4K textures and PBR materials that plug directly into physics engines for scalable scene composition and robotic training.
Concerns
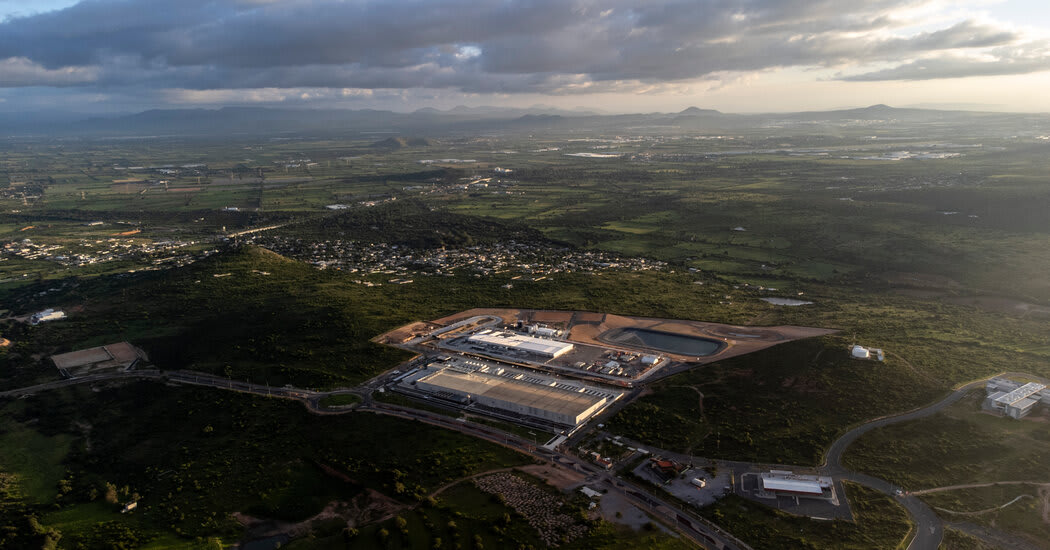
From Mexico to Ireland, Fury Mounts Over a Global A.I. Frenzy. Residents near new AI data centers report increased power and water outages that disrupted schools, healthcare, and daily life as the industry’s rapid expansion places extra strain on local infrastructure.
Hundreds of public figures, including Apple co-founder Steve Wozniak and Virgin’s Richard Branson urge AI ‘superintelligence’ ban. A new letter urges a moratorium on efforts to build AI that could outperform humans across most cognitive tasks until there is broad public backing and scientific consensus that such systems can be developed and controlled safely.
These nonprofits lobbied to regulate OpenAI — then the subpoenas came. Several nonprofits that criticized OpenAI’s shift from nonprofit to for-profit say the company has issued broad subpoenas demanding extensive financial records and communications, sparking concerns that litigation is being used to intimidate critics and burden small advocacy groups with legal costs.
Reddit sues Perplexity for allegedly ripping its content to feed AI. Oxylabs says it was named in Reddit’s lawsuit without prior contact and defends its lawful public-data collection business, arguing it provides compliant infrastructure used by researchers and businesses and will contest the allegations.
Wikipedia says traffic is falling due to AI search summaries and social video. The Wikimedia Foundation says the drop—about an 8% year-over-year decline in human page views—stems from generative AI answers in search and younger users turning to social video, warning this could reduce volunteer editors and donors unless platforms encourage more click-throughs and attribution.
Bryan Cranston and SAG-AFTRA say OpenAI is taking their deepfake concerns seriously. OpenAI has apologized for unintended deepfake generations, tightened its opt-in likeness and voice guardrails, and pledged to review complaints, while industry groups and SAG-AFTRA push for legal protections like the proposed NO FAKES Act.
The AI sexting era has arrived. People are using chatbots across platforms to seek erotic relationships, raising safety, mental-health, and regulatory concerns as companies monetize sexualized AI features.
Read More in Last Week in AI